创建索引
根据mysql表信息同步创建es索引
1、字段映射
[field]
#不区分大小写
test.product.title = text
[mapping]
#不区分大小写
#数值类型
TINYINT = short
SMALLINT = integer
MEDIUMINT = integer
INT = integer
INTEGER = integer
BIGINT = long
FLOAT = float
DOUBLE = double
DECIMAL = double
#日期类型
DATE = date
TIME = date
YEAR = date
DATETIME = date
TIMESTAMP = date
#字符串类型
CHAR = keyword
VARCHAR = keyword
TINYBLOB = keyword
TINYTEXT = keyword
BLOB = keyword
TEXT = keyword
MEDIUMBLOB = keyword
MEDIUMTEXT = keyword
LONGBLOB = keyword
LONGTEXT = keyword
#默认
default = keyword
[es-python]
#不区分大小写
short = int
integer = int
long = int
float = float
double = float
date = str
keyword = str
text = str
[type]
#由于date format 所以对应value区分大小写
#通用
text.type = text
text.analyzer = ik_max_word
keyword.type = keyword
long.type = long
integer.type = integer
short.type = short
byte.type = byte
double.type = double
float.type = float
half_float.type = half_float
scaled_float.type = scaled_float
date.type = date
date.format = yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss||yyyy-MM-dd||epoch_millis
field:schema+mysql表名+字段名对应的es 字段类型
mapping:mysql默认数据类型对应的es类型
es-python:数据插入是的转换方式
type:es对应类型的的信息补充
mysql表字段转换es类型是先查field配置下有没有,有就直接确定类型,没有就按mysql类型找到默认的es类型,找到类型之后再从type中找到确定的type
以下类为读取配置:核心方法get_field_type()找到mysql字段对应es类型
import configparser
config = configparser.RawConfigParser()
config.read("./field.ini", encoding='utf-8')
fieldList = []
resultList = config.items("field")
class Field:
def __init__(self, schema_name=None, table_name=None, field_name=None, field_type=None):
self.schema_name = schema_name
self.table_name = table_name
self.field_name = field_name
self.field_type = field_type
def set_schema_name(self, schema_name):
self.schema_name = schema_name
def set_table_name(self, table_name):
self.table_name = table_name
def set_field_name(self, field_name):
self.field_name = field_name
def set_field_type(self, field_type):
self.field_type = field_type
def parse(self, value):
value = str(value)
result_list = value.split(".")
self.set_schema_name(result_list[0])
self.set_table_name(result_list[1])
self.set_field_name(result_list[2])
class ESType:
def __init__(self, es_index=None, es_type=None, es_analyzer=None, es_format=None):
self.es_index = es_index
self.es_type = es_type
self.es_analyzer = es_analyzer
self.es_format = es_format
def set_es_index(self, es_index):
self.es_index = es_index
def set_es_type(self, es_type):
self.es_type = es_type
def set_es_analyzer(self, es_analyzer):
self.es_analyzer = es_analyzer
def set_es_format(self, es_format):
self.es_format = es_format
for temp in resultList:
item = Field()
item.parse(str(temp[0]).lower())
item.set_field_type(str(temp[1]).lower())
fieldList.append(item)
typeList = config.items("type")
typeMap = {}
for temp in typeList:
keyList = str(temp[0]).lower().split(".")
if keyList[0] not in typeMap:
typeMap[str(keyList[0]).lower()] = {}
typeMap[str(keyList[0]).lower()][keyList[1]] = str(temp[1])
mysql_es_mapping = {}
mappingList = config.items("mapping")
for temp in mappingList:
mysql_es_mapping[str(temp[0]).lower()] = str(temp[1]).lower()
es_python_mapping = {}
es_python_mapping_list = config.items("es-python")
for temp in es_python_mapping_list:
es_python_mapping[str(temp[0]).lower()] = str(temp[1]).lower()
def get_field_type_name(schema_name, table_name, field_name):
for temp in fieldList:
if temp.schema_name != schema_name:
continue
if temp.table_name != table_name:
continue
if temp.field_name != field_name:
continue
return temp.field_type
return None
def get_field_type(schema_name, table_name, field_name, field_type):
schema_name = schema_name.lower()
table_name = table_name.lower()
field_name = field_name.lower()
field_type = field_type.lower()
type_name = get_field_type_name(schema_name, table_name, field_name)
type_name = str(type_name).lower()
if type_name in typeMap:
return typeMap[type_name]
elif field_type in mysql_es_mapping:
if mysql_es_mapping[field_type] in typeMap:
return typeMap[mysql_es_mapping[field_type]]
else:
return typeMap[mysql_es_mapping['default']]
return None
def convert_data_from_es_to_python(value, field_type):
if field_type in mysql_es_mapping:
result_type = mysql_es_mapping[field_type]
else:
result_type = mysql_es_mapping['default']
result_type = str(result_type)
if result_type in es_python_mapping:
mapping_type = str(es_python_mapping[result_type])
return convert(value, mapping_type)
def convert(value, result_type):
if value is None:
return None
if 'str' == result_type:
return str(value)
elif 'int' == result_type:
return int(value)
elif 'float' == result_type:
return float(value)
else:
return str(value)
# print(json.dumps(fieldList, ensure_ascii=False, default=lambda obj: obj.__dict__, sort_keys=True, indent=4))
# print(json.dumps(typeMap, ensure_ascii=False))
# print(get_field_type("test", "product", "num", "int"))
创建索引
import json
import pymysql.cursors
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
import configUtil
import fieldConfig
schema = configUtil.schema
tableList = configUtil.table_list
es = Elasticsearch(
[configUtil.esUrl],
# 认证信息
# http_auth=(configUtil.esUser, configUtil.esPassword)
)
# 连接数据库
connect = pymysql.Connect(
host=configUtil.dbHost,
port=configUtil.dbPort,
user=configUtil.dbUser,
passwd=configUtil.dbPassword,
db=schema,
charset='utf8'
)
cursor = connect.cursor()
def getMapping(schema, tableName):
sql = """
select aa.COLUMN_NAME,aa.DATA_TYPE,aa.COLUMN_COMMENT, cc.TABLE_COMMENT
from information_schema.`COLUMNS` aa LEFT JOIN
(select DISTINCT bb.TABLE_SCHEMA,bb.TABLE_NAME,bb.TABLE_COMMENT
from information_schema.`TABLES` bb ) cc
ON (aa.TABLE_SCHEMA=cc.TABLE_SCHEMA and aa.TABLE_NAME = cc.TABLE_NAME )
where aa.TABLE_SCHEMA = '%s' and aa.TABLE_NAME = '%s'
"""
data = (schema, tableName,)
cursor.execute(sql % data)
fields = {}
for row in cursor.fetchall():
type = str(row[1])
name = str(row[0])
field_type = fieldConfig.get_field_type(schema, tableName, name, type)
fields[str(row[0])] = field_type
return fields
for table in tableList:
fieldMapping = getMapping(schema, table)
mappings = {
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 0
},
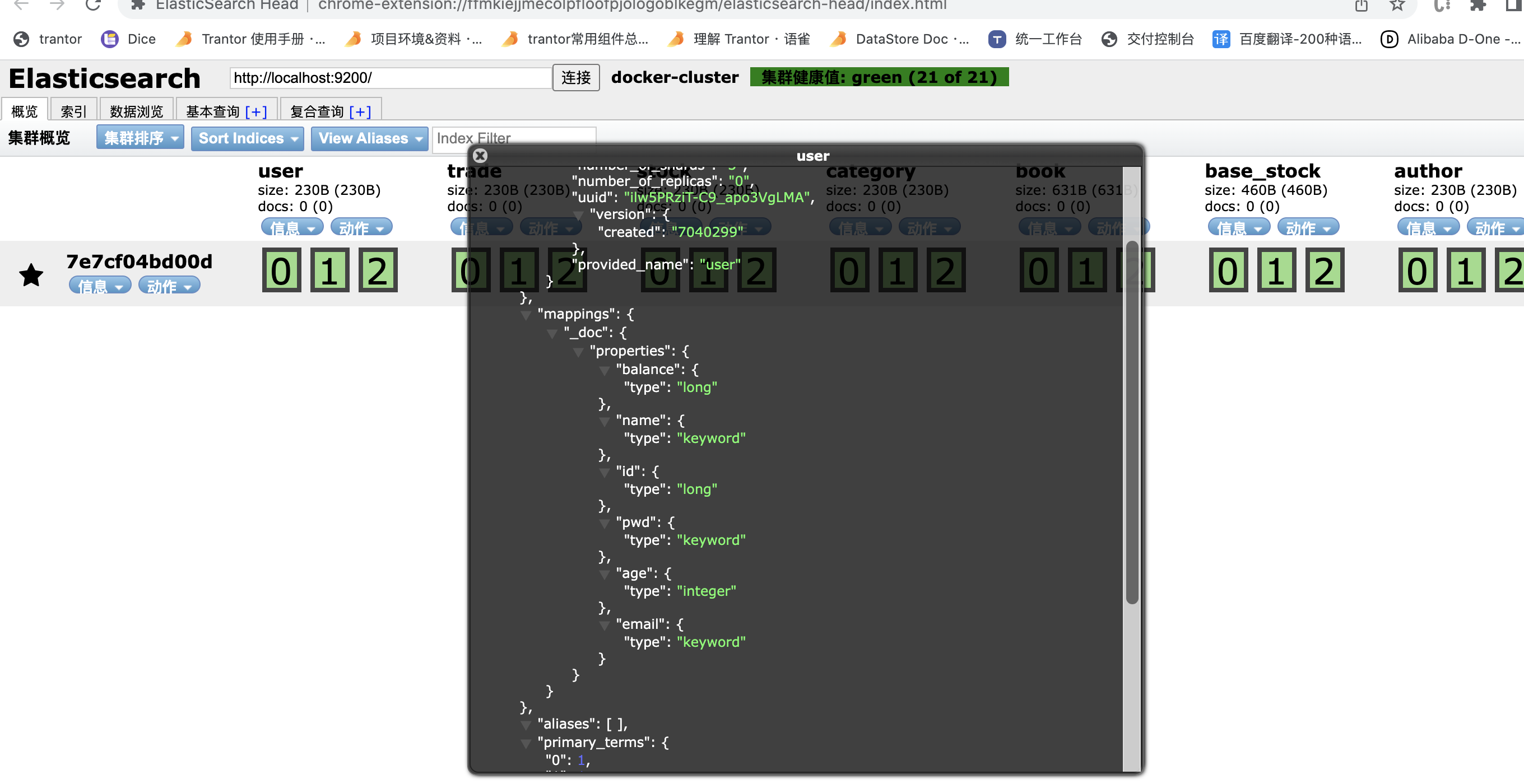
"mappings": {
"properties": fieldMapping
}
}
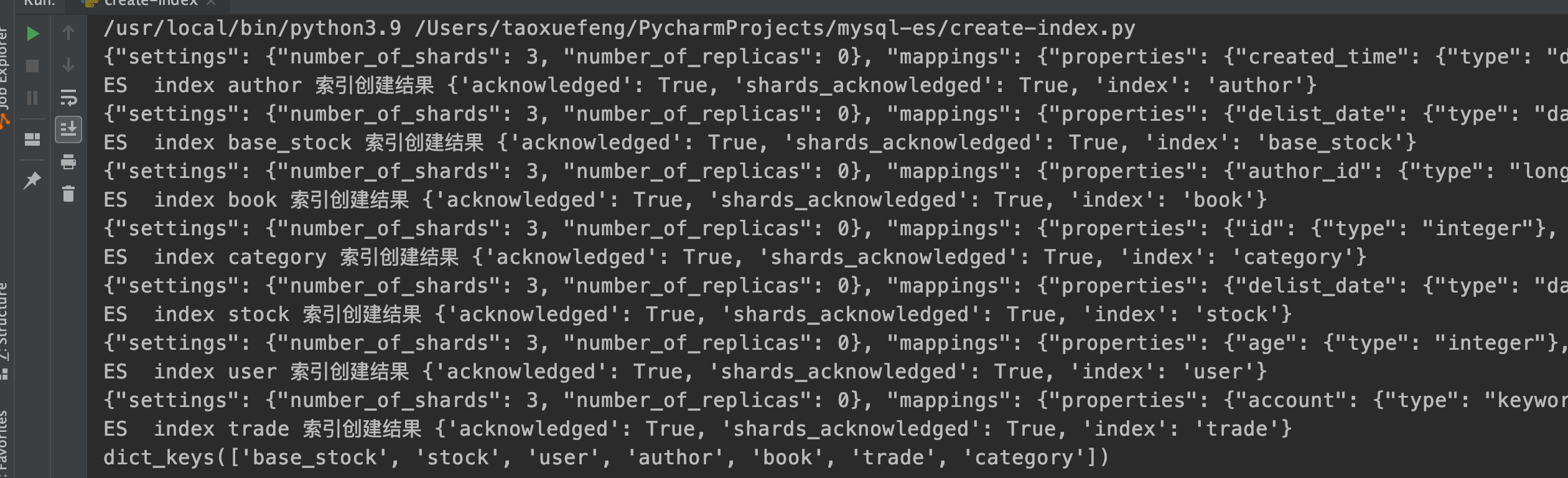
print(json.dumps(mappings))
res = es.indices.create(index=table, body=mappings)
print("ES index " + table + " 索引创建结果 " + str(res))
print(es.indices.get_alias().keys())
索引删除:快速重建
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
import configUtil
es = Elasticsearch(
[configUtil.esUrl],
# 认证信息
# http_auth=(configUtil.esUser, configUtil.esPassword)
)
tableList = configUtil.table_list
print(es.indices.get_alias().keys())
for table in tableList:
isExist = es.indices.exists(table)
if isExist:
es.indices.delete(index=table)
print(table)
print(es.indices.get_alias().keys())